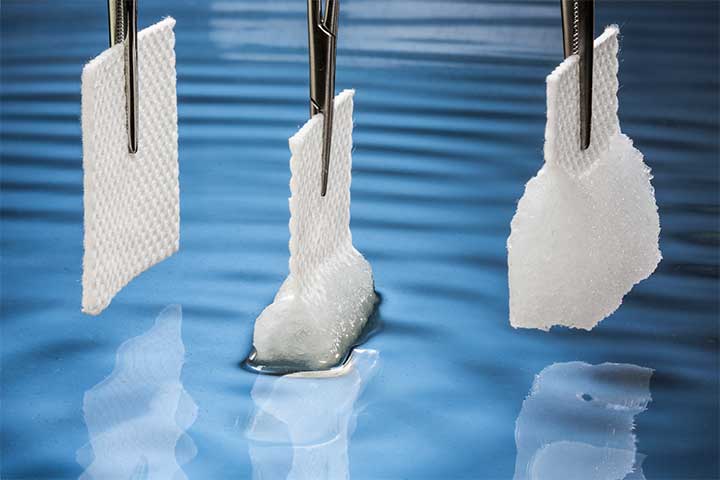
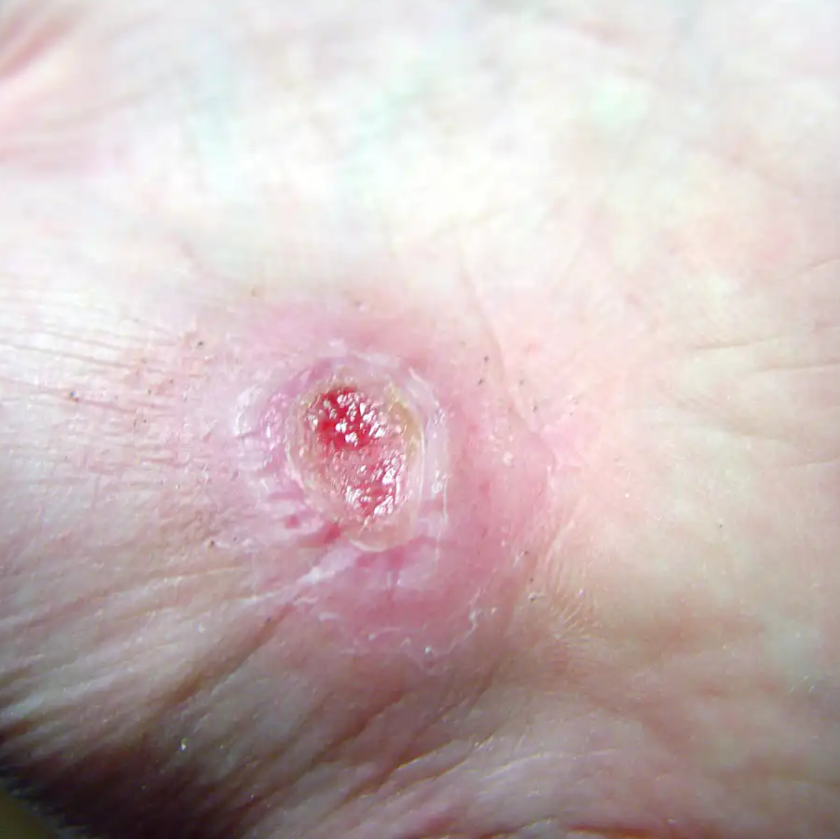
The cutting-edge of wound care is a progressively flexible one, where textiles, foams, and films are applied to wound management technology with the goal of synergistic physiological function. These innately intuitive materials underpin the emerging medical solutions that practitioners and their patients are finding more effective than traditional wound care and closure methods. With an aging population more frequently seeking medical care and a surge in diabetes diagnoses, market analysts predict a continuing rise in demand for advanced wound care management products, fueling an annual industry growth rate of 6.4% over the next five years.
Flexible Materials in Chronic Wound Treatment
Advanced flexibility delivers improved quality of life.
Particularly well-suited to the treatment of complex and chronic wounds, customized thin films, nonwovens, advanced textiles, foams, and adhesives provide a foundation for holistic wound management plans. Patients with access to advanced wound care experience:
- Decreased tissue maceration and scarring with wound dressings designed to maintain a moist wound environment.
- Increased levels of physical activity while in recovery as a benefit of the wound dressing’s flexibility and conforming characteristics.
- Improved pain management through wound contact layer administered medications and/or non-stick, soothing flexible material surfaces.
- Extended potential for hygienic at-home care by means of patient-friendly high exudate wound dressings that need changing less frequently.
These advanced wound care and closure methods promote rapid healing and provide relief post-operative recoveries, recurring lesions, and compounding medical bills due to repeated treatments and hospital visits.
Flexible Materials in Specialized Wound Management
Highly customizable materials maximize practitioner efficiency.
Healthcare practitioners are experiencing expanded availability of advanced wound care and closure alternatives. With the ability to tailor the properties of flexible materials for specialized wound management applications, product developers are introducing improved reliability and efficiency into healthcare practitioners’ procedures.
Surgeons have reported a decrease in post-operative infections due to the use of adhesive, mesh, and film rather than traditional closure methods. This is attributed to a decrease in the time required to complete the closure procedure as well as the improved ability to visually monitor the wound during after-care. Moreover, wound sterilization, in general, becomes more reliable when composite dressings include antimicrobials – in the adhesives, as coated film barriers, or impregnated foam.
Flexible Materials in Transdermal Medication
Flexible materials also provide the means for transdermal medication, independent of, or integrated into, a wound dressing contact layer. This relieves the stress of digestive disruption caused by oral ingestion of antibiotics and painkillers, which can adversely affect recovery time and patient well-being.
read more: sourcebookmaterials.com